Continuous / Batch type Solvent Extraction Plant
Technology
Continuous / Batch type Solvent Extraction Plant
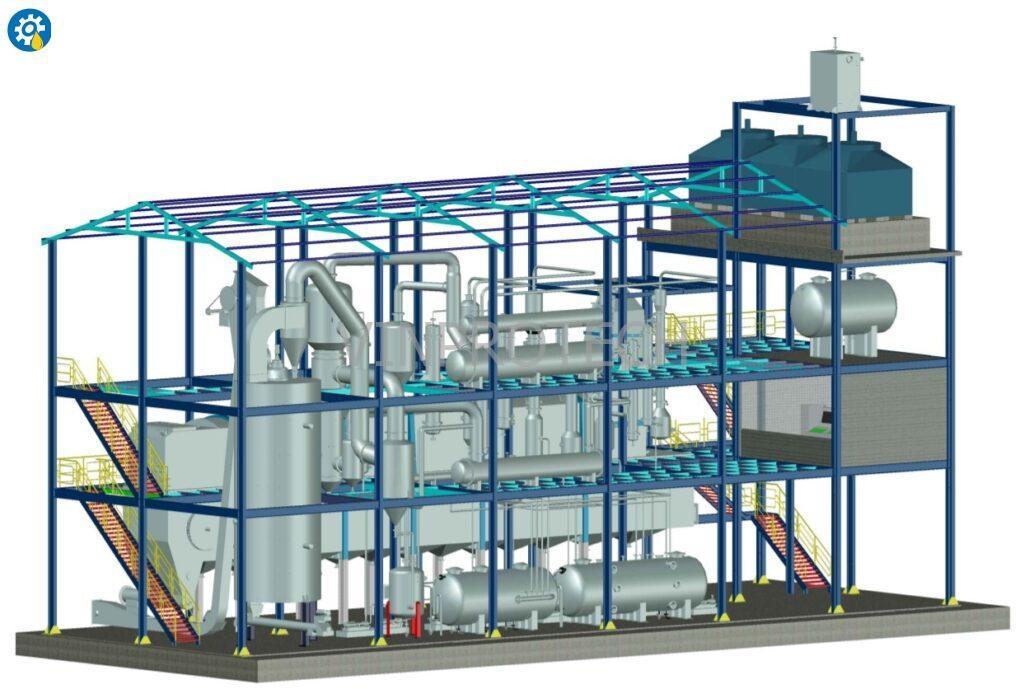
Continuous / Batch type Solvent Extraction Plant 3D Visualization
Solvent extraction is the process of extracting oil from seeds and other oil-containing materials using a solvent. At VINPROTECH, we specialize in manufacturing and exporting solvent extraction plants. Our plants utilize food-grade n-Hexane solvent, derived from petroleum, ensuring the highest quality extraction.
Renowned for our well-established design, our solvent extraction plants are cost-effective, robust, and user-friendly. They offer flexibility for seamless transition of process materials, all while integrating advanced safety features.
The final product of our solvent extraction plants is low-temperature oil, prized for its excellent color and high bleach-ability properties. This makes it the perfect choice for subsequent refining processes. Trust VINPROTECH for top-tier solvent extraction solutions The solvent extraction process involves three main stages
Renowned for our well-established design, our solvent extraction plants are cost-effective, robust, and user-friendly. They offer flexibility for seamless transition of process materials, all while integrating advanced safety features.
The final product of our solvent extraction plants is low-temperature oil, prized for its excellent color and high bleach-ability properties. This makes it the perfect choice for subsequent refining processes. Trust VINPROTECH for top-tier solvent extraction solutions The solvent extraction process involves three main stages


